

Transportation equipment, such as cars and trucks, is capital. Tools such as hammers, screwdrivers, and wrenches are also capital. Modern versions of the first stone tools include saws, meat cleavers, hooks, and grinders all are used in butchering animals. Those tools were the first capital because they were produced for use in producing other goods-food and clothing. We know that very early on, however, they began shaping stones into tools, apparently for use in butchering animals. Long ago, when the first human beings walked the earth, they produced food by picking leaves or fruit off a plant or by catching an animal and eating it. The other is to increase the amount of human capital possessed by workers. One is to increase the total quantity of labor, either by increasing the number of people available to work or by increasing the average number of hours of work per time period.

The amount of labor available to an economy can be increased in two ways. Workers who are gaining skills through experience or through training are acquiring human capital.
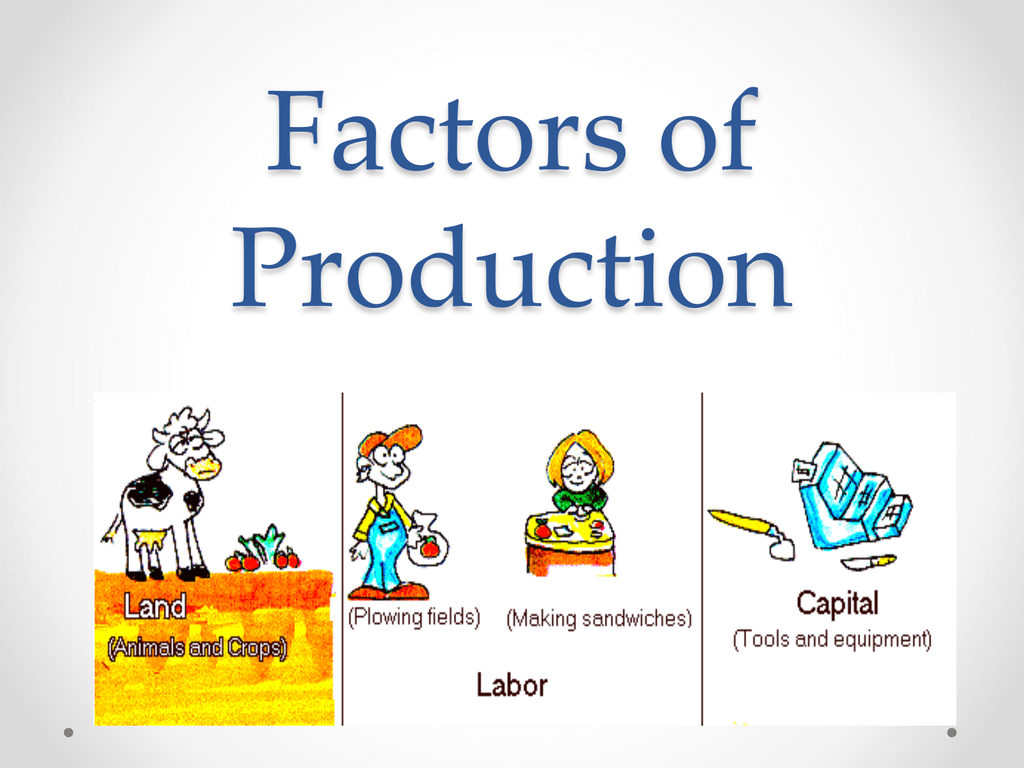
Skills a worker has as a result of education, training, or experience that can be used in production are called human capital The skills a worker has as a result of education, training, or experience that can be used in production. It is the natural ability an untrained, uneducated person brings to a particular production process. The first is the human equivalent of a natural resource. In some contexts, it is useful to distinguish two forms of labor. People who would like to work but have not found employment-who are unemployed-are also considered part of the labor available to the economy. People who work to repair tires, pilot airplanes, teach children, or enforce laws are all part of the economy’s labor. Labor is the human effort that can be applied to production. As economists began to grapple with the problems of scarcity, choice, and opportunity cost more than two centuries ago, they focused on these concepts, just as they are likely to do two centuries hence. We will then look at the roles played by technology and entrepreneurs in putting these factors of production to work. The three basic building blocks of labor, capital, and natural resources may be used in different ways to produce different goods and services, but they still lie at the core of production. In the next three sections, we will take a closer look at the factors of production we use to produce the goods and services we consume.
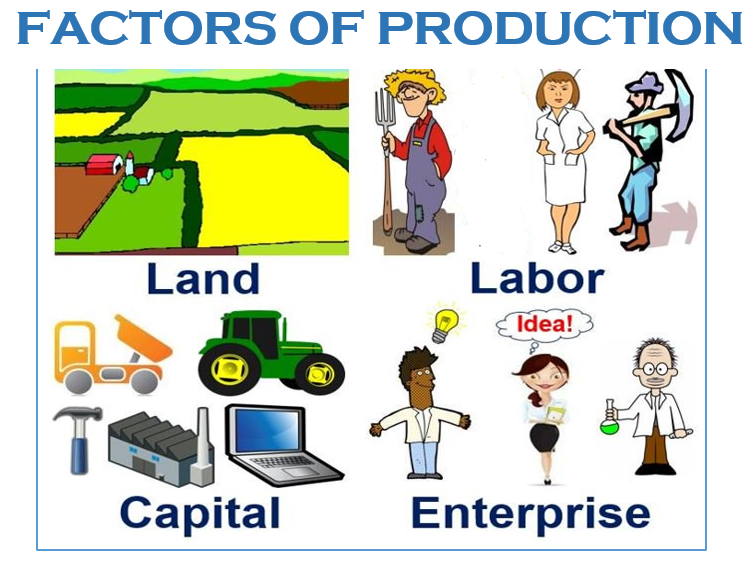
are the resources of nature that can be used for the production of goods and services. Natural resources The resources of nature that can be used for the production of goods and services. Office buildings, machinery, and tools are examples of capital. is a factor of production that has been produced for use in the production of other goods and services. Capital A factor of production that has been produced for use in the production of other goods and services. People who are employed-or are available to be-are considered part of the labor available to the economy. is the human effort that can be applied to the production of goods and services. Labor The human effort that can be applied to the production of goods and services. The factors of production in an economy are its labor, capital, and natural resources. Ultimately, then, an economy’s factors of production create utility they serve the interests of people. The value, or satisfaction, that people derive from the goods and services they consume and the activities they pursue is called utility The value, or satisfaction, that people derive from the goods and services they consume and the activities they pursue. Explain the role of technology and entrepreneurs in the utilization of the economy’s factors of production.Ĭhoices concerning what goods and services to produce are choices about an economy’s use of its factors of production The resources available to the economy for the production of goods and services., the resources available to it for the production of goods and services.Define the three factors of production-labor, capital, and natural resources.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
